scaffold
Scaffolding is a working platform erected to ensure the smooth progress of building construction. It is used for the operation of workers and to solve vertical and horizontal transportation. It is widely applied in the fields of constructio...
Scaffolding is a working platform erected to ensure the smooth progress of building construction. It is used for the operation of workers and to solve vertical and horizontal transportation. It is widely applied in the fields of construction, advertising, municipal engineering, transportation roads and bridges, mines, etc.
Classification
According to the erection location: The external scaffolding is erected along the periphery of the building and is used for the masonry and decoration of the external walls; the internal scaffolding is erected inside the construction object and is used for the masonry of the walls on each floor and internal decoration.
According to the materials: The wooden scaffolding has a relatively low cost, but its stability and safety are poor; the bamboo scaffolding is light but easily affected by the environment; the steel pipe scaffolding has high strength and good stability and is widely used; the aluminum alloy scaffolding is light and corrosion-resistant and is suitable for scenarios such as interior decoration.
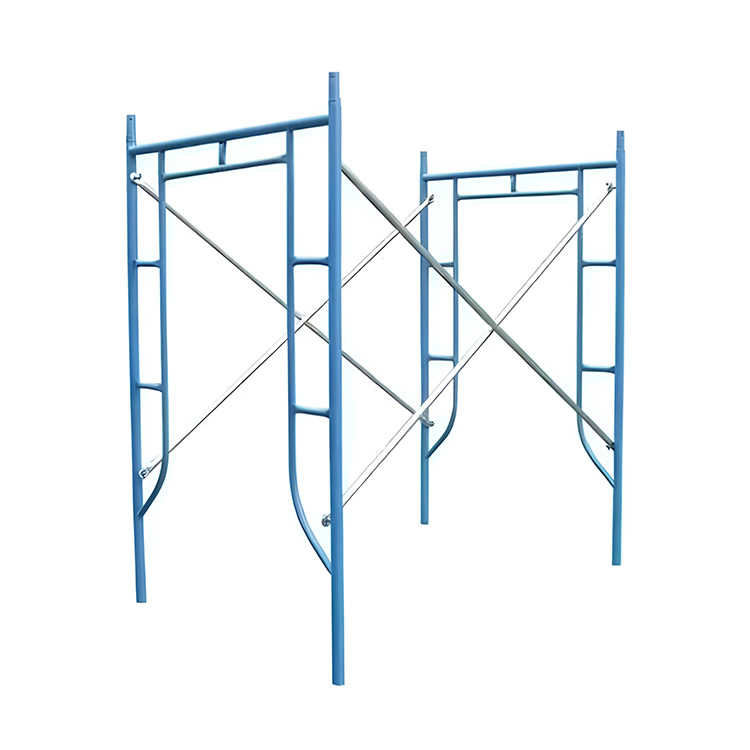
According to the structural form: The standing pole type scaffolding is composed of standing poles, crossbars, etc.; the bridge type scaffolding takes the bridge-shaped structure as the main load-bearing component; the portal scaffolding has various uses and can be used to erect external scaffolding, construction operation platforms, etc.; the suspended scaffolding suspends the working platform in the air through steel wire ropes or chains, etc.
Component Composition
Basic structure: It is the part of the framework that directly bears and transmits vertical loads and their internal forces, and is composed of basic structural units such as rectangular planar grids and rectangular three-dimensional grids.
Overall tie members: Including diagonal members, cross braces and horizontal reinforcing members, etc., which can make the scaffolding form a stable framework and enhance the ability to resist lateral forces.
Components of the working layer: There are working platform surfaces and outer protective materials such as scaffold planks, toe boards, and railings, which are used to provide a working platform and safety protection.
Other safety protection measures: Including the protection of entrances and exits and various safety fences, safety nets, etc.
Wall attachment: It is an important measure to improve the stable bearing capacity of the scaffolding and prevent overturning, and there are various forms such as wire attachment and steel pipe attachment.
Support facilities: Used to support the scaffolding and transmit the loads to the engineering structure, such as base plates, pedestals, etc.
Erection Requirements
Foundation: The ground should be flat and firm. Base plates should be used when necessary. The foundation part of the scaffolding often needs to be compacted, hardened, etc.
Standing poles: The spacing should be determined according to the type of scaffolding, the erection height, etc. The standing poles at the bottom should be arranged in a staggered manner with steel pipes of different lengths, and the vertical deviation should be controlled within the specified range.
Crossbars: The spacing of the main crossbars in the height direction of the scaffolding is generally not more than 1.8 meters. The two ends of the small crossbars are fixed on the standing poles to form a spatial structure.
Cross braces: They should be set at both ends of the outer facade of the scaffolding. The net distance between each cross brace in the middle should not be more than 15 meters, and the diagonal members are preferably lap-jointed when lengthened.
Wall connection members: They must be set when the height of the scaffolding exceeds 6 meters. They should be evenly distributed according to the vertical scaffolding surface. The maximum vertical spacing should not exceed 8 meters, and the maximum coverage area of each point should not exceed 40 square meters.
Contents of Safety Inspection
It includes inspections of aspects such as structural integrity, load-bearing capacity, protection measures, working platforms, ladders and passages, foundation stability, electrical safety, environmental factors, etc.